Лабораторная работа: Measuring specific latent heat of vaporization of water
Trial4 m=0.05kg t=192s
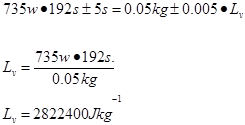
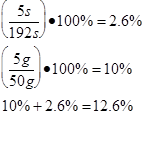
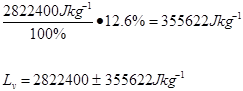
Trial 5 m=0.05kg t=189s
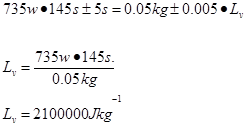
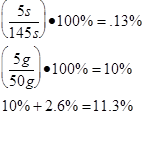
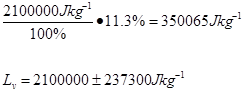
Average
| Trials | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Lv /Jkg-1 |
2.7 x 106 ±349110 |
2.6 x 106 ±338688 |
2.8 x 106 ±355622 |
2.6 x 106 ±338688 |
2.1 x 106 ±237300 |
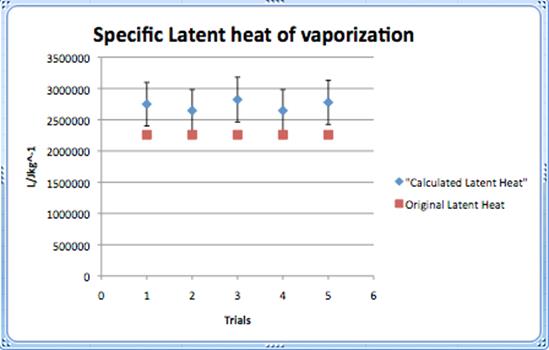
Conclusions and evaluations
The calculated value of the specific latent heat of vaporization was supposed to be 2.3 x 106 J/Kg. Unfortunately the results achieved by the calculations were not perfect and did not reach the accepted values. All the Lv calculated were in one range, but did not come close to 2.3 x 106.
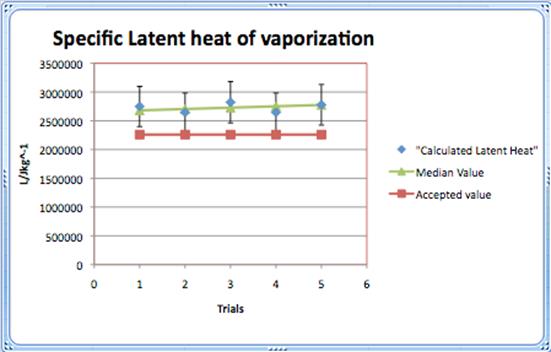
The median value of the calculated Latent heat of vaporization was modelled by the equation
y= 25520x+2657760
and showed that the values were still inflated, but regarding the uncertainty, some values reached the accepted value.
The reasons of such weak results were the uncertainties of the procedure, and old equipment. The scientist didn’t have a set time to start timing the boiling water, therefore the time could be the reason of the misleading calculations. The scales that the scientist was usingwere three-beam, and not electronic. This could as well be a reason of the uncertain mass. It was difficult for the scientst to measure the exact moment,when the water had evaporated 50 grams of water.
Reasonable improvements for this experiment would be, setting a time for the scientist to start measuring